K-BESS solution: Unlocking energy storage with Airborne Wind Energy in remote locations
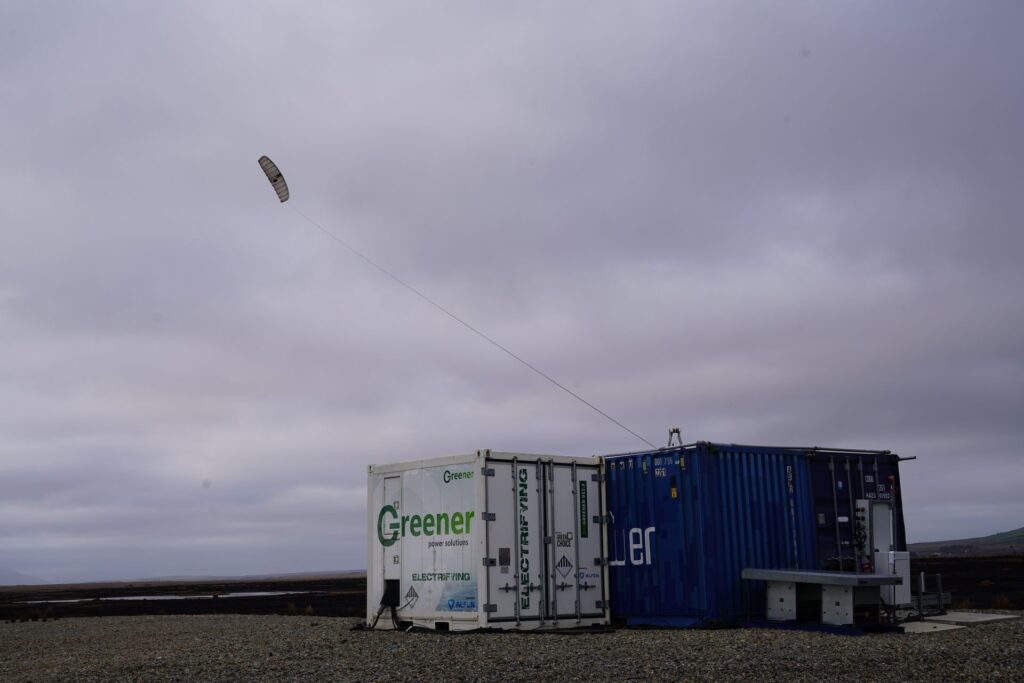

K-BESS System
Kite-powered Battery Energy Storage System (K-BESS) is emerging as a versatile and game-changing solution to supply renewable electricity in temporary, remote, or hard-to-electrify locations. By combining AWE systems with on-site battery storage, K-BESS addresses energy needs where traditional grids cannot reach.
The DEM-AWE Route-to-Market Report, developed under the Interreg NWE-funded DEM-AWE project, was recently launched to provide the first comprehensive commercial roadmap for deploying K-BESS across Northwest Europe. The report outlines a market-driven strategy to scale AWE through a mobile and off-grid solution designed to replace diesel generators.
K-BESS: Enabling clean power where the grid cannot reach
This hybrid system targets three high-impact markets:
- Infrastructure construction sites – highways, railways, and dykes with high energy needs, limited grid access, and strong decarbonisation pressure.
- Quarries – rural and energy-intensive operations, increasingly subject to regulations promoting on-site electrification.
- Islands – areas where grid connection is technically or economically unfeasible, leaving diesel as the default energy source.

Kitepower
Market sizing and commercial forecast
The report evaluates Netherlands, Germany, France, Ireland, and the UK using bottom-up data, stakeholder interviews, and GIS-based spatial analysis to estimate K-BESS deployment potential. Key insights include:
- Construction sites represent the strongest early market, with over 300 K-BESS units projected by 2030, led by the Netherlands, Germany, and France.
- Quarries in Germany and France could see 80 additional units, driven by emissions regulations and the shift to on-site renewables.
- Islands present strategic opportunities for up to 60 units, particularly in line with the EU’s “Clean Energy for EU Islands” initiative.
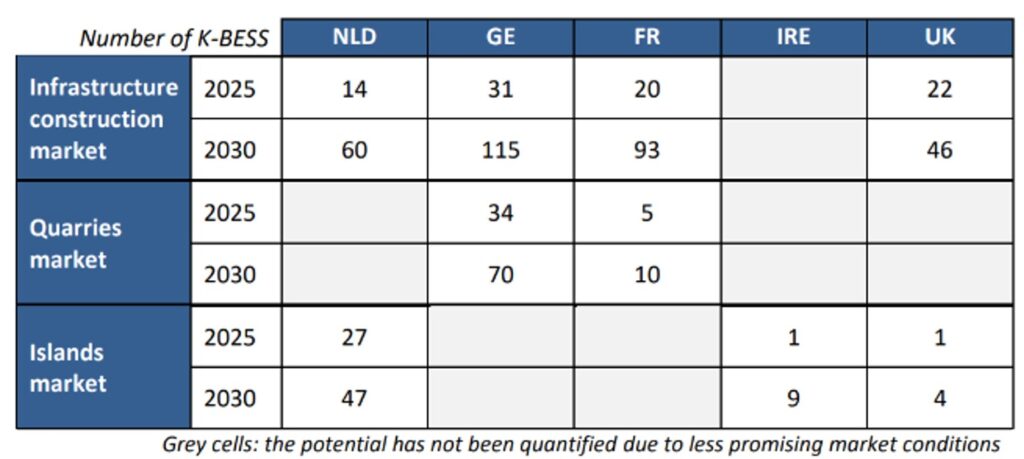
The total market potential by 2030 exceeds 450 units for Kitepower’s K-BESS alone, expecting to offer a lower Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCoE) than diesel in multiple regions, especially where green energy incentives are applied.
Strategic role in AWE commercialisation
K-BESS serves a dual purpose: an early revenue-generating product and a technology validation platform. By enabling real-world performance testing, it builds operator confidence and supports gradual scaling toward grid-connected AWE farms.
The system leverages a 30 kW AWE demonstrator by Kitepower, capable of charging a 400 kWh battery in under 10 hours. It is currently being tested by partners such as Dura Vermeer (Netherlands) and RWE (Ireland) in real construction and grid-constrained scenarios.
Commercial strategy and recommendations
To accelerate deployment, the report proposes a pragmatic route-to-market:
- Prioritise remote infrastructure projects, where energy costs and grid limitations favour K-BESS.
- Engage early adopters in construction and extractive industries to validate the model and generate visibility.
- Pursue pilot projects and public procurement aligned with climate goals.
- Integrate AWE in broader renewable planning for resilient island energy systems.
Written by:

